Types of Fasteners [with Pictures]

What is Fasteners?
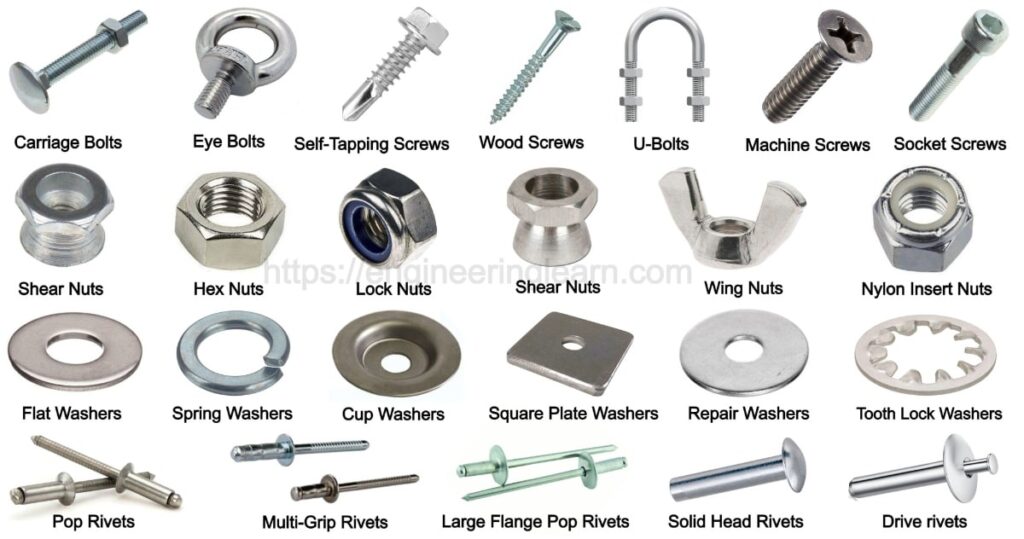
Types of Fasteners [with Pictures] :- Fasteners are the mechanical units which are used to join two or more objects together. Fasteners can be used to join either permanently or temporarily depending upon the site condition. There are numerous types of fasteners with different applications, about which one should definitely know.
Fasteners are categorized as Permanent or temporary units.
Example for permanent fasteners can be rivets, nails etc. which are single-use fasteners designed to join two objects permanently. Thus, these fasteners once installed cannot be removed, removing it can lead to destroy it. Whereas, temporary fasteners are designed to join two or more objects temporarily and can be removed and reused easily.
Example of temporary fasteners are bolts and screws which are commonly used in a number of industries and products as they allow the parts to re-assemble whenever required. Temporary fasteners are also known as threaded or non-threaded.
Types of Fasteners
- Threaded Fasteners
- Nuts
- Washers
- Rivets
A) Threaded Fasteners: ( Types of Fasteners )
These are the most commonly used fasteners mostly for assembling components which can be installed or removed as per the need. There are three most commonly used threaded fasteners i.e. Bolts, Screws and Studs. Let understand each of them in detail.
1. Bolts: ( Types of Fasteners )
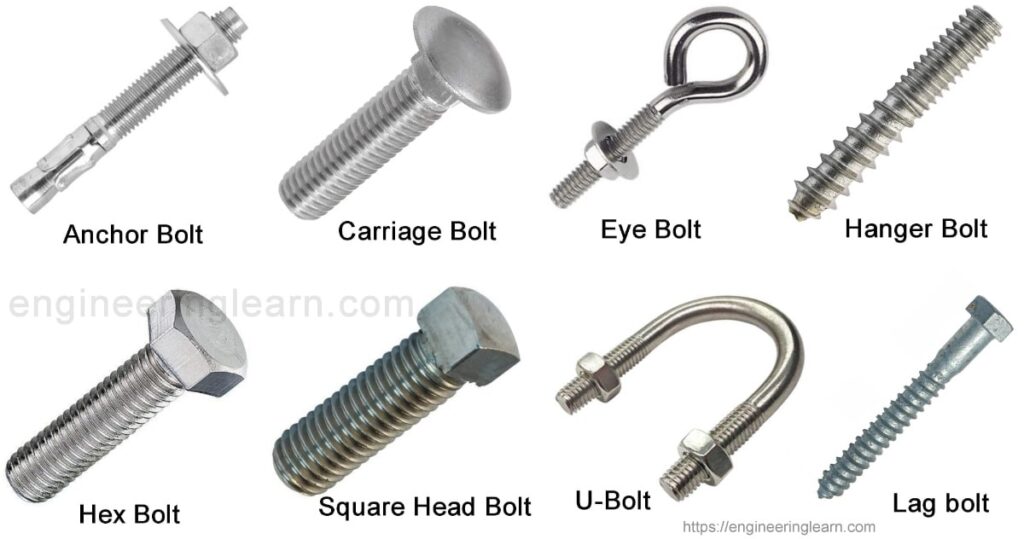

Bolts are the ones which has a head on its one end, usually the hex head and are threaded on the other. These are usually used in combination with a nut or a washer to hold the material in the exact place.
2. Screws: ( Types of Fasteners )
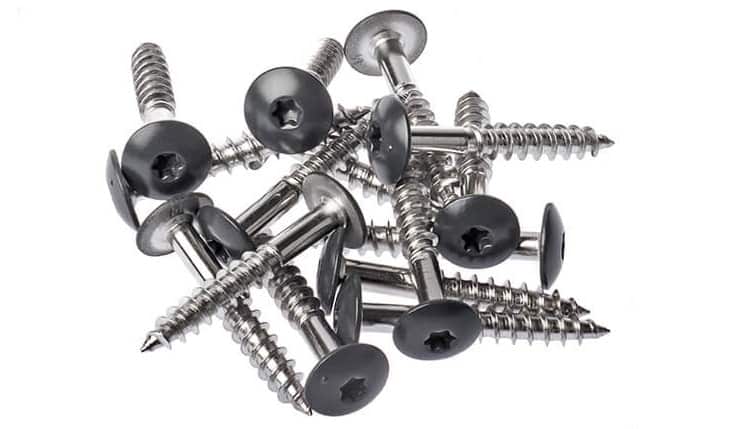

Screws are quite similar to the bolts which also has a head on one end and a thread on the other head. They main difference is that screws are used to screw into a threaded hole. There are various types of screws which can be used according to the site requirement, like cap screws, machine screws, wood screws etc.
3. Studs: ( Types of Fasteners )
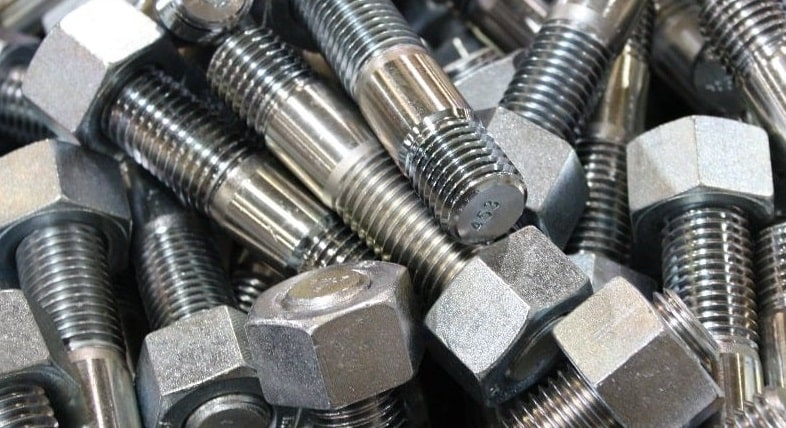

Studs are different from bolts and screws as they are threaded on the both ends, and thus do not have any head. This component is used to compile internally threaded holes together.
Types of Threaded Fasteners
1. Bolts and Set Screws

Bolts and Set screws are usually found having a hexagonal head accompanied with a thread which can easily be used in conjunction with a nut or a threaded hole. Bolts are generally found having a shank beneath the head, whereas set screws are threaded till the head.
2. Carriage Bolts

Carriage bolts are also known as cup square hex bolts which have a smooth rounded head and a square beneath. These fasteners are usually used to hold metal to wood.
3. Eye Bolts
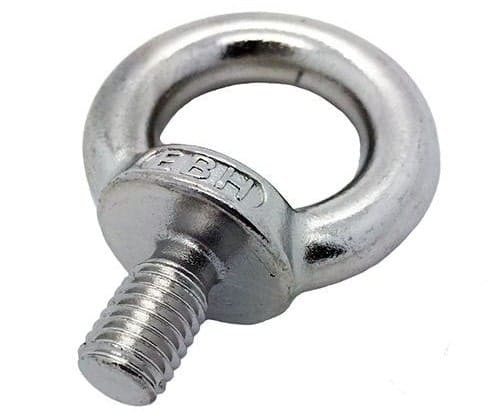

Eye bolts have a circular ring instead of a traditional head and are used to fix chain to any surface.
4. U-Bolts

U bolts are used for upholding round objects such as pipes, tubes to the wall or any other surface.
5. Wood Screws
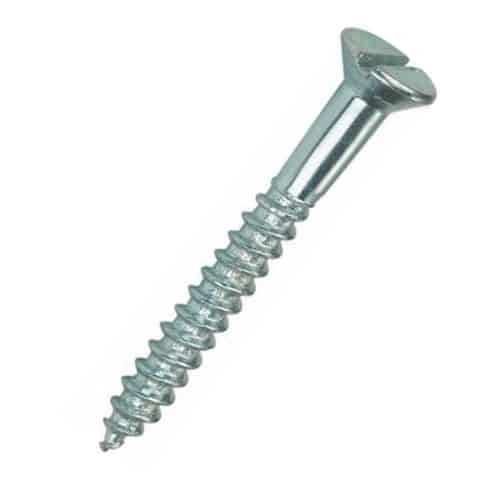

Wood screws are used in wood and come in various head shapes which can be selected according to the requirement.
6. Machine Screws
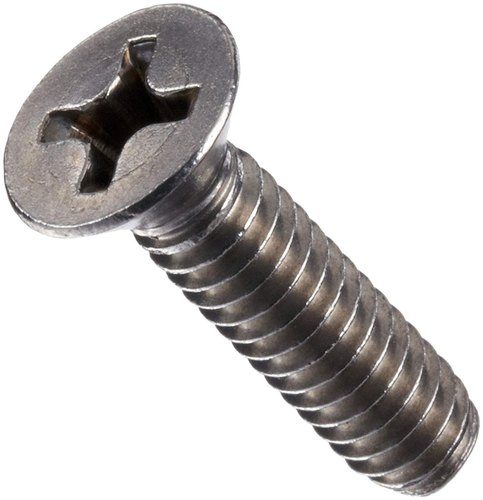

Machine Screws are accompanied with a nut or tapped hole.
7. Self-Tapping Screws
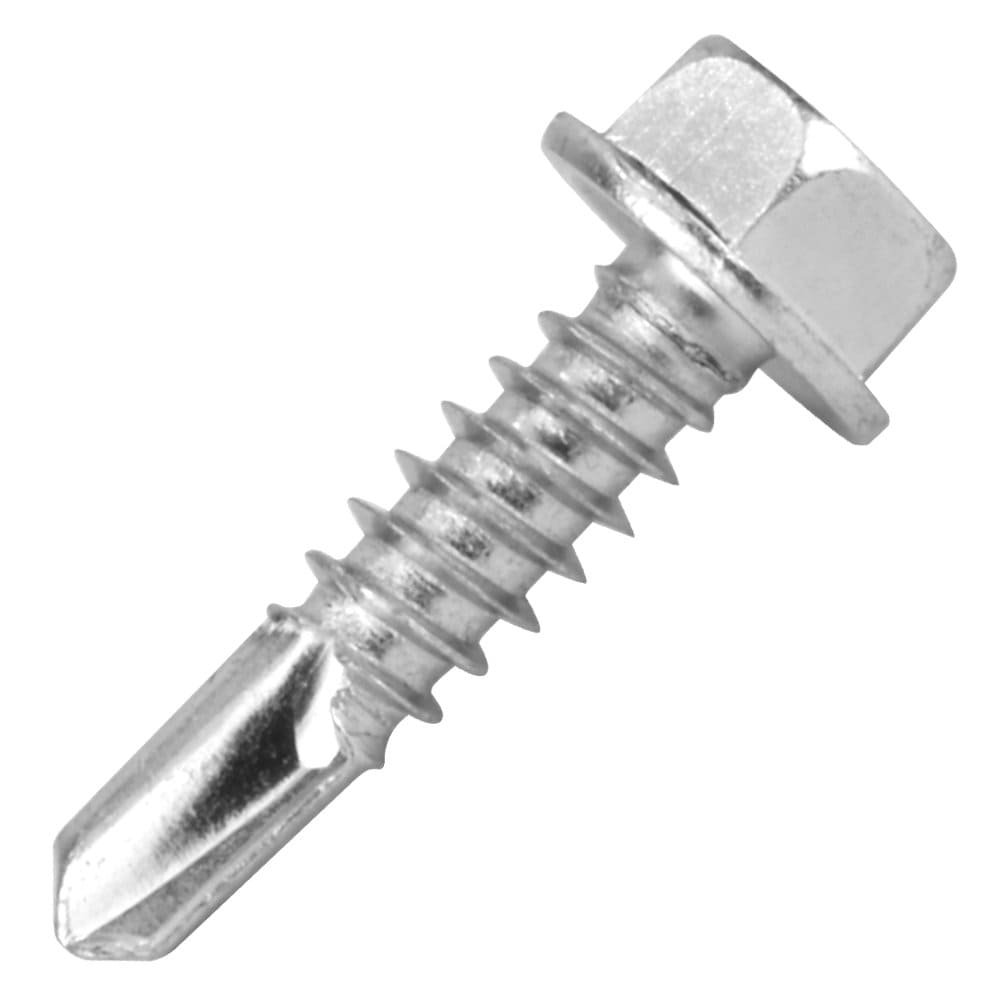

Also known as self-tappers, these screws are mostly used in metal sheets.
8. Socket Screws
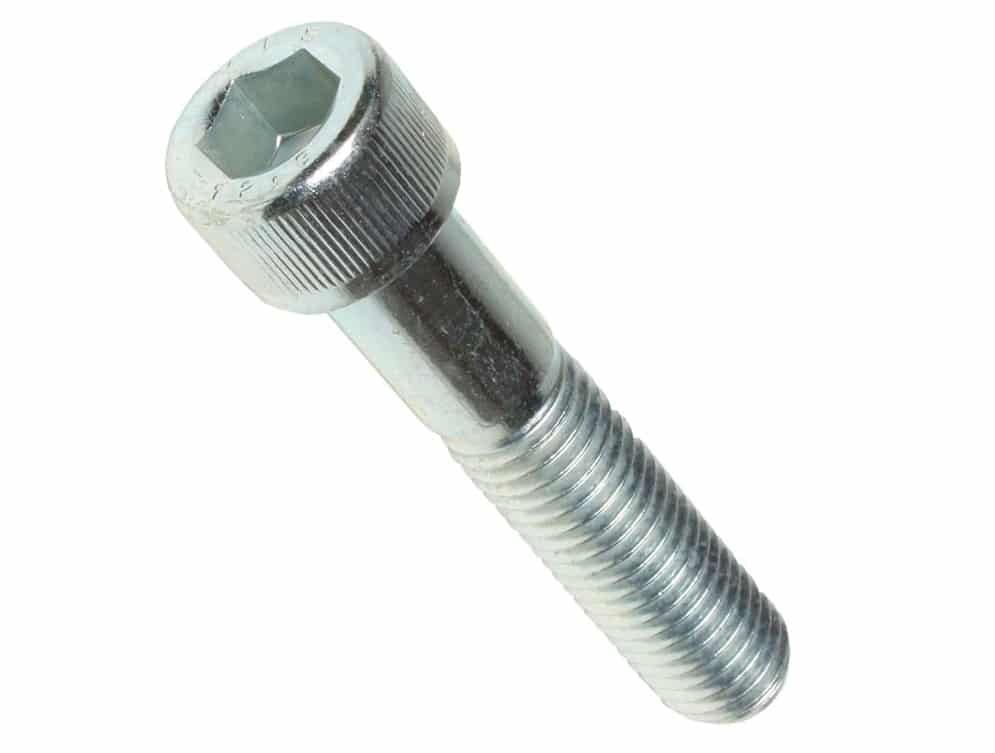

Socket screws feature a smooth shank and has an Allen head which are fastened using an Allen key only. Socket screws are available in a different head shape like button, socket cap and counter sunk.
9. Grub Screws
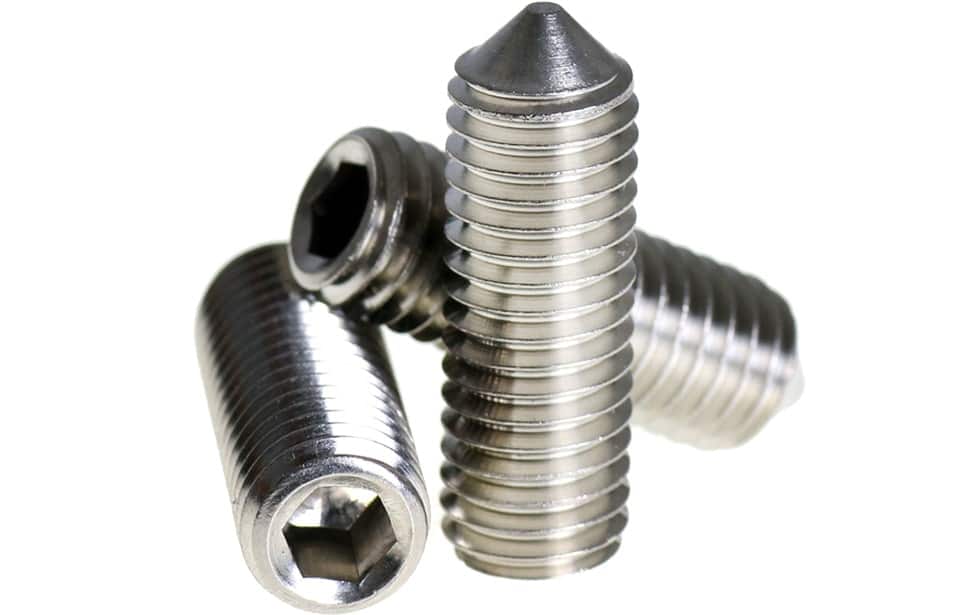

Grub screws are a special type of screw which are found to have no head. These screws are used at the places where there needs to be no movement or rotation between two parts.
B) Nuts: ( Types of Fasteners )
Nuts are used with a bolt to join two or more mechanical parts together. The most commonly known nut is a hexagonal nut, but there are various other types of nuts which are used according to the site requirement.
1. Hex Nuts

Hexagonal nuts have an internal thread in them. These are the most common type of nuts, and are used in almost all types of industries with various applications.
2. Lock Nuts
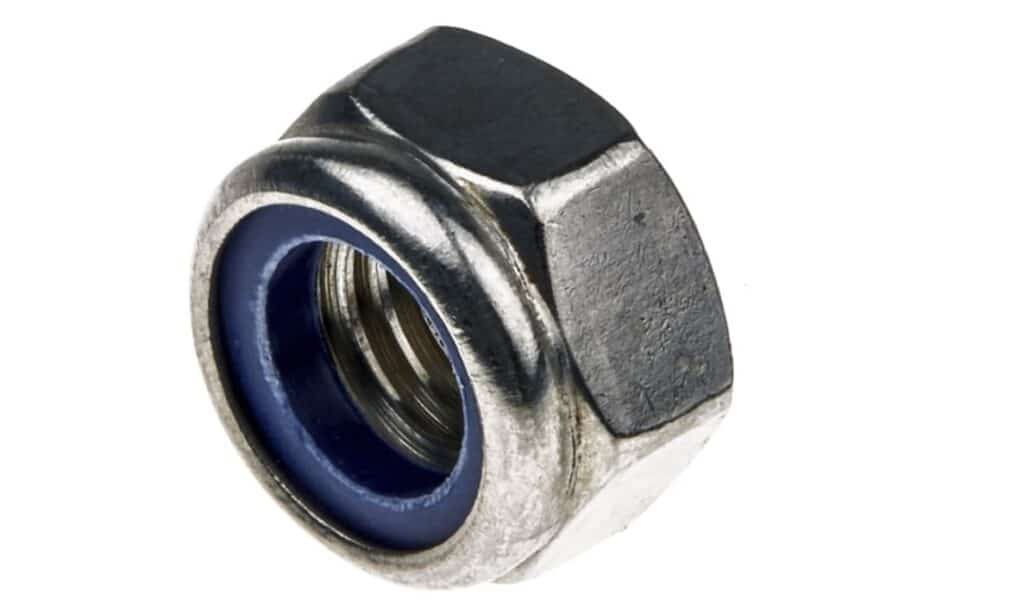

Lock nuts are used to lock the nut in place without clamping any another object.
3. Nylon Insert Nuts

Well known as Nylon nut, these nuts have a nylon insert which does not let the nut loose due to the effect of vibration.
4. Shear Nuts

Shear nuts have a hexagonal gripping point which snaps off during the maximum torque, leaving just the nut which is quite difficult to remove.
5. Wing Nuts
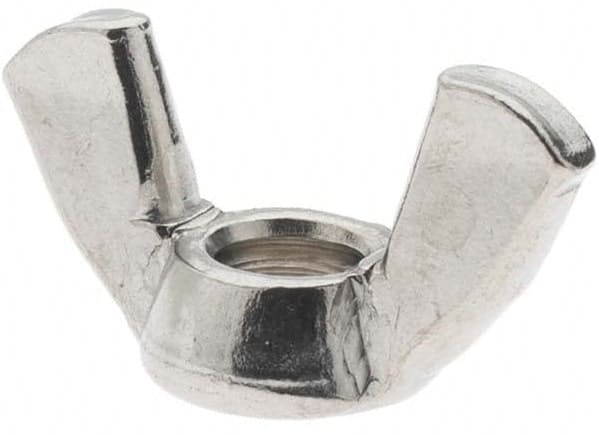

Wing nuts are commonly used in applications where the nut needs to be removed frequently. These nuts have two external “wings shaped face” which allows for easy manual turning.
C) Washers: ( Types of Fasteners )
Washers are the units which are commonly used between the head of a bolt, screw, nut and any material which is being clamped. The main function of a washer is to increase the bearing area of the head and meanwhile also protect the material from any sort of damage. There are numerous types of Washers, with different uses and functions.
1. Flat Washers

Flat washers are the most common type of washers which are used to evenly distribute the load of the bolt, screw or nut.
2. Spring Washers

Spring washers or locking washers are designed to resist the bolt, screw or nut from losing with the effect of vibration.
3. Cup Washers

Cup Washers are mostly used in conjunction with a wood screw depending upon the requirement of the site.
4. Repair Washers

Commonly known as Penny or Fender Washers. These washers have a small diameter hole and are designed to create a greater bearing surface in order to prevent pull-through.
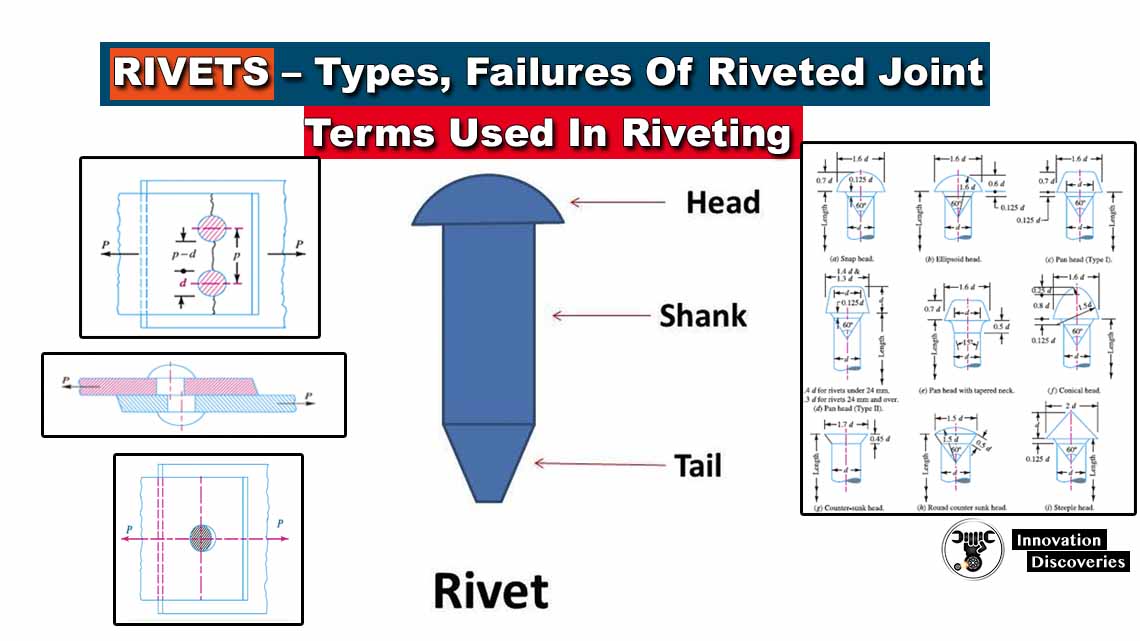
D) Rivets: ( Types of Fasteners )
Rivets are categorized in permanent fasteners, which once installed cannot be removed or reused. Rivets are used in various industries to fulfil various applications but are most commonly used to join metal sheets and plates.
1. Pop Rivets
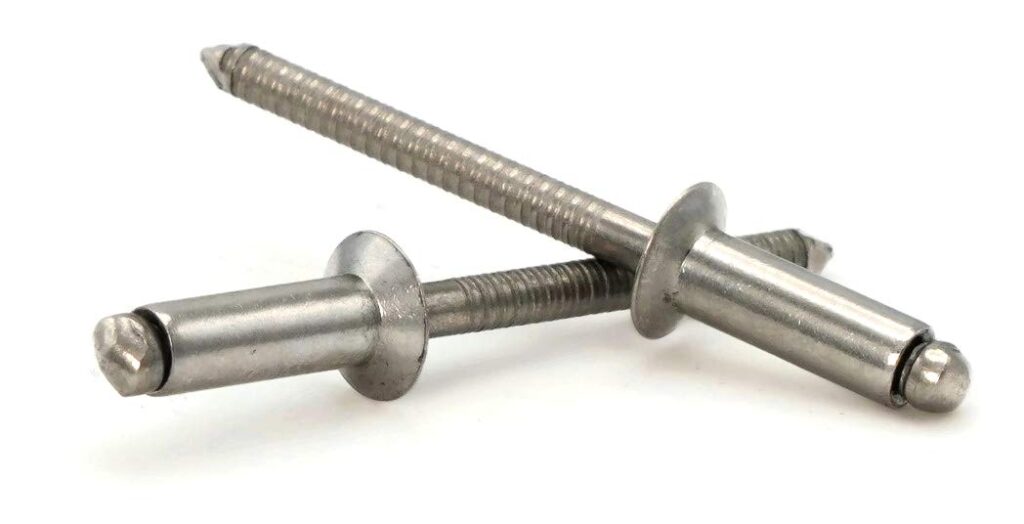

Pop rivets consists of a hat and a mandrel. These rivets are used to join two mechanical materials together during installation.
2. Large Flange Pop Rivets
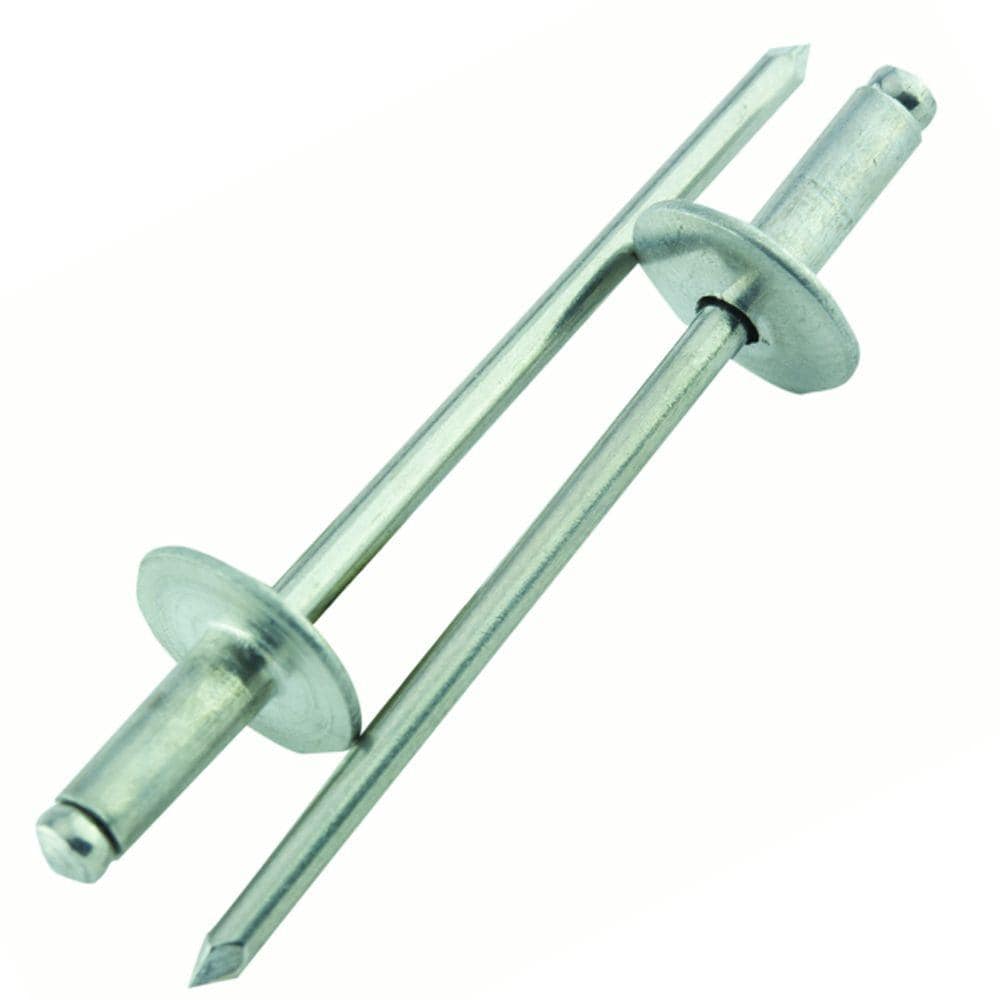

Large Flange Pop Rivets are very similar to Pop Rivets in their applications but offers various features as compared to Pop rivets.
3. Multi-Grip Rivets

Multi grip rivets are used to join materials with varying thickness, which would normally require various rivet sizes. These rivets are found to be versatile and cost-effective.